A Comprehensive Guide to Calendar Spreads and How to Use Them as a Powerful Trading Strategy
Last updated on:
 |
| Source: Calendar Spread (wallstreetmojo.com) |
A Comprehensive Guide to Calendar Spreads and How to Use Them as a Powerful Trading Strategy
Introduction: What is a Calendar Spread and How Does it Work?
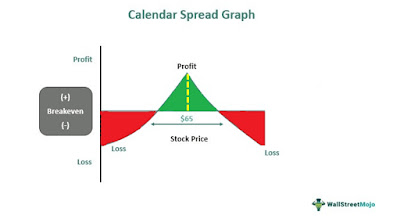
Calendar spreads are among the most popular options strategies used by traders. They involve buying and selling options of the same underlying asset but with different expiration dates. Traders can use calendar spreads to capitalize on different market conditions, such as when they expect a particular stock to remain range-bound or when they expect a stock to make a big move in either direction. It is also known as a time spread and is used to capitalize on the expected movement of the underlying stock over time. For example, to buy a calendar spread on AAPL stock, one might choose to sell a front month call option and then purchase a back month call option. AAPL's current spot price is $100. If the spot price of AAPL moves up by 2% in the month the options are in-the-money, then this is called time value profit. The profit will increase as more time passes and more points move in your favor. Additionally, an out-of-the money strike (like 100) would be used if you think that there is going to be too much movement before expiration.
Analyzing the Different Types of Calendar Spreads and Their Benefits
There are four main types of calendar spreads: bullish calendar spread, bearish calendar spread, diagonal calendar spreads, and vertical calendar spreads. Each type has its own unique benefits and drawbacks that traders should consider before entering into any trade. In this section, we will analyze the different types of calendar spreads and their respective benefits. and drawbacks.
Bullish Calendar Spread
Benefits
- Allows traders to limit risk while potentially profiting from a decline in price
- Benefit from time decay, as it will cause the value of calls to decrease faster than the put
- Reduce trading capital requirements, as only one put needs to be purchased
- Benefit from any upside potential in the stock by collecting the premium from selling the calls
Bearish Calendar Spread
A bearish calendar spread is an options trading strategy in which a trader buys a call option at a certain strike price and expiration date, and then sells a call option of the same strike price but with a later expiration date. This strategy allows the trader to profit from a decrease in the underlying stock’s price over the course of the two options’ expiration dates.
Benefits
- The trader can benefit from a decrease in the underlying stock’s price over the course of the two options’ expiration dates
- The risk associated with the bearish calendar spread is limited, since the trader will be able to buy back the earlier expiration call option at the same strike price
- By selling the later expiration call option, the trader will be able to collect a premium which will offset the cost of the earlier expiration call option
Diagonal Calendar Spread
A diagonal calendar spread is an options trading strategy in which a trader buys a call option with a certain strike price and expiration date and then sells a call option of a different strike price but with the same expiration date. The trader profits from a decrease in the underlying stock’s price over the course of the two options’ expiration dates.
Benefits
- The trader can benefit from a decrease in the underlying stock’s price over the course of the two options’ expiration dates
- The risk associated with the diagonal calendar spread is limited, since the trader can buy back the earlier expiration call option at the same strike price
- By selling the later expiration call option, the trader will be able to collect a premium which will offset the cost of the earlier expiration call option
- The trader will have a reduced risk of time decay, since the spread is made up of two different strike prices
Vertical Calendar Spread
A vertical calendar spread is an options trading strategy in which a trader buys a call option at a certain strike price and expiration date and then sells a call option of the same strike price but with a later expiration date. The trader profits from an increase in the underlying stock’s price over the course of the two options’ expiration dates.
Benefits
- The trader is able to benefit from an increase in the underlying stock’s price over the course of the two options’ expiration dates
- The risk associated with the vertical calendar spread is limited, as the maximum loss is limited to the cost of the spread (the difference between the two options’ prices)
- The trader can take advantage of volatility as the spread can benefit from a larger move in the underlying stock price
- The spread allows traders to benefit from time decay, as the option with the longer expiration date will lose value faster than the option with the shorter expiration date, thus increasing the spread’s value
The Pros & Cons of Utilizing Calendar Spreads in Your Trading Portfolio
Pros of Using Calendar Spreads
- Reduced risk: With calendar spreads, you only invest the difference between the two option prices, which minimizes risk.
- Leverage: You can use a calendar spread to leverage the movement of the underlying asset while controlling the cost of the options used.
- Reduced volatility: By using a calendar spread, you can take advantage of the time decay of the options, reducing overall volatility.
- Increased probability of winning: By using a calendar spread, you are increasing the probability of winning due to the decreased risk and volatility.
- Tax savings: By utilizing a calendar spread, you can lower your tax bill by taking advantage of the lower premiums of the options.
- Increased liquidity: By trading a calendar spread, you can increase your liquidity by taking advantage of the increased liquidity of the options.
- Flexibility: Calendar spreads give you the flexibility to use different strategies based on market conditions.
- Portfolio diversification: A calendar spread strategy can help diversify your trading portfolio and reduce risk.
Cons of Using Calendar Spreads
- Spread width: If the spread width is too wide, you will not be able to make a profit on the spread.
- Time decay: The time decay of the option can work against you if the market moves in an unexpected direction.
- Complexity: Trading calendar spreads can be complex and requires some knowledge of options trading.
- Losses: You can still incur losses even with the reduced risk of trading a calendar spread.
- Fees: You will need to pay fees for the options used in a calendar spread strategy.
- Volatility: Although the volatility is reduced, it can still be a factor when trading a calendar spread.
- Leverage: Leverage can work against you if the market moves in an unexpected direction.
- Low returns: The returns for a calendar spread can be relatively low compared to other options trades.
Calendar Spread Strategy Examples to Help You Master This Powerful Trading Tool
Example #1: Short Calendar Spread Trade
Suppose it is currently January and you believe that the stock XYZ will stay relatively stable in price for the next month but will fall significantly in the following month. You can set up a short calendar spread trade by doing the following:
Sell one February XYZ call option with a strike price of $50 for $3 per share.
In this trade, you are betting that the price of XYZ will not rise above $50 by the end of February. The net cost of the trade is $2 per share ($5 for the March call minus $3 for the February call). If the price of XYZ remains stable or falls slightly in February, the February call will expire worthless, and you will keep the entire premium received from selling the call. The March call will retain some value due to its longer expiration date. If the price of XYZ falls significantly in March, the value of the March call will increase, and you can sell it for a profit. If the price of XYZ rises above $50 in February, the value of the February call will increase, and you may have to buy it back at a loss.
Example #2: Long Calendar Spread Trade
Suppose it is currently January, and you believe that the stock ABC will rise in price by the end of the year, but you don't want to risk too much capital upfront. You can set up a long calendar spread trade by doing the following:
Buy one December ABC call option with a strike price of $100 for $10 per share.
In this trade, you are betting that the price of ABC will rise by the end of the year but will not rise significantly by the end of January. The net cost of the trade is $5 per share ($10 for the December call minus $5 for the January call). If the price of ABC remains relatively stable in January, the January call will expire worthless, and you will keep the entire premium received from selling the call. The December call will retain some value due to its longer expiration date. If the price of ABC rises significantly by the end of the year, the value of the December call will increase, and you can sell it for a profit. If the price of ABC does not rise significantly, the value of the December call will decline, but you still have the option of holding onto it until expiration.
Managing, Adjusting and Hedging a Calendar Spread Trade
Managing a Calendar Spread Trade
One of the keys to managing a calendar spread trade is to monitor the price movements of the underlying asset and adjust your positions accordingly. For example, if the price of the underlying asset rises significantly, the value of the call option in a long calendar spread trade will increase, and the value of the put option in a short calendar spread trade will decrease. In this case, you may want to consider closing out your position or rolling your options forward to a later expiration date to capture more profit.
Similarly, if the price of the underlying asset falls significantly, the value of the call option in a short calendar spread trade will increase, and the value of the put option in a long calendar spread trade will decrease. In this case, you may want to consider adjusting your position by buying back the short option or rolling it forward to a later expiration date.
Adjusting a Calendar Spread Trade
Adjusting a calendar spread trade involves modifying the strike price or expiration date of the options to reflect changes in market conditions. For example, if you have a long call option with a strike price of $50 and the underlying asset rises to $55, you may want to adjust your position by buying a new call option with a higher strike price or rolling your existing option forward to a later expiration date.
Similarly, if you have a short put option with a strike price of $50 and the underlying asset falls to $45, you may want to adjust your position by selling a new put option with a lower strike price or rolling your existing option forward to a later expiration date.Hedging with a Calendar Spread Trade
Hedging with a calendar spread trade involves using options to offset potential losses in the underlying asset. For example, if you have a long position in a stock that you believe may fall in price, you can hedge your position by buying a put option with a strike price and expiration date that corresponds to your existing position. This creates a calendar spread trade, which can help offset potential losses in your stock position if the price of the underlying asset falls.
Similarly, if you have a short position in a stock that you believe may rise in price, you can hedge your position by buying a call option with a strike price and expiration date that corresponds to your existing position.
Managing and hedging a calendar spread trade is essential to minimize risk and maximize profits. By monitoring market conditions and adjusting your positions accordingly, you can take advantage of market inefficiencies and generate income with this trading strategy.
Risks Involved with Trading Calendar Spreads and How to Manage Them
Trading calendar spreads can be a lucrative way to generate income from the options market. However, as with any trading strategy, there are risks involved. In this section, we'll discuss some of the most significant risks associated with trading calendar spreads and how to manage them.
Volatility Risk When Trading Spreads
One of the most significant risks involved with trading calendar spreads is volatility risk. This is the risk that the underlying asset will experience significant price movements, making it challenging to predict the future value of the options. As a result, the value of the options in your spread can change rapidly, making it challenging to manage your position.
To manage volatility risk, it's essential to have a solid understanding of the market conditions and potential catalysts that could affect the price of the underlying asset. This includes factors such as economic data releases, geopolitical events, and news about the company or industry. By keeping up with these developments and adjusting your positions accordingly, you can help manage your exposure to volatility risk.Option Expiration Risk
Another significant risk when trading calendar spreads is option expiration risk. This is the risk that the options in your spread will expire before you can realize your desired profit. This risk is especially relevant in short-term calendar spreads, where the options have a shorter expiration date.
To manage option expiration risk, it's essential to have a clear exit strategy in place. This includes setting specific profit targets and stop-loss orders, as well as monitoring the value of the options in your spread closely. If the options are nearing expiration and you haven't realized your desired profit, it may be necessary to close out your position and reevaluate your trading strategy.Liquidity Risk in Calendar Spread Trades
Liquidity risk is another risk associated with trading calendar spreads. This is the risk that there won't be enough buyers or sellers in the market to execute your trade at a reasonable price. This can result in wider bid-ask spreads, which can reduce the profitability of your spread.
To manage liquidity risk, it's essential to trade options with high trading volumes and open interest. This helps ensure that there are enough buyers and sellers in the market to execute your trade at a reasonable price. Additionally, it's important to be patient and avoid chasing trades, as this can increase your exposure to liquidity risk.Managing Risk in Calendar Spreads
Finally, the key to managing risk when trading calendar spreads is to have a solid understanding of the underlying asset and the options market. This includes developing a clear trading plan and sticking to it, monitoring market conditions, and being disciplined in managing your positions.
It's also important to diversify your trading strategies and not rely solely on calendar spreads to generate income. By diversifying your portfolio, you can help spread your risk and limit potential losses.
Trading calendar spreads can be a lucrative way to generate income from the options market. However, it's essential to be aware of the risks involved and take steps to manage those risks effectively. By being disciplined in your approach and monitoring market conditions closely, you can help minimize your exposure to risk and maximize your potential profits.
The Low Down
In conclusion, calendar spreads are a powerful trading strategy that can help generate income from the options market. By utilizing the knowledge gained from this comprehensive guide, traders can develop a deeper understanding of calendar spreads and how they can be used to maximize profits while minimizing risks. It's important to remember that calendar spreads are not a one-size-fits-all solution, and they must be tailored to fit individual trading styles and market conditions. Additionally, successful trading requires discipline, patience, and a willingness to adapt to changing market conditions. With the right approach, calendar spreads can be an excellent addition to a trader's arsenal and a valuable tool for achieving their financial goals.Disclosure:
Ramy Capital is in an affiliate agreement with Marketfy/Benzinga for a share of revenue. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own truthful opinions. Ramy Capital trades with our own wheel strategy. We have attended demo training sessions of this course and are very confident in the knowledge and teaching ability of the instructor. The information and recommendation provided do not serve, either directly or indirectly, as financial advice. Trading options may not be suitable for your specific situation. Past performance is not indicative of future performance. Your results trading these strategies could be negative. Trading options involve risk.
Additional Disclosure:
The views expressed in this article are the opinions of the author as of the date of publication. Opinions are subject to change without notice and the author is under no obligation to update their views on this blog. This is not financial advice and is being provided for informational purposes only. You should not rely solely on the information or opinions provided in our content, rather use them as starting points for your own due diligence and draw your own conclusions based on your own research. The author cannot guarantee the veracity or completeness of any information provided in this blog and will not be responsible for inadvertent errors or omissions.
Comments
Post a Comment